Revolutionizing Conservation Efforts: Giant Panda Skin Cells Transformed into Stem Cells
In a groundbreaking development in the field of conservation biology, researchers in China have successfully reprogrammed skin cells from giant pandas into induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). This achievement holds immense promise for the preservation of this iconic endangered species by paving the way for the creation of primordial germ cells that can serve as precursors to sperm and egg cells, crucial for the reproduction and survival of giant pandas.
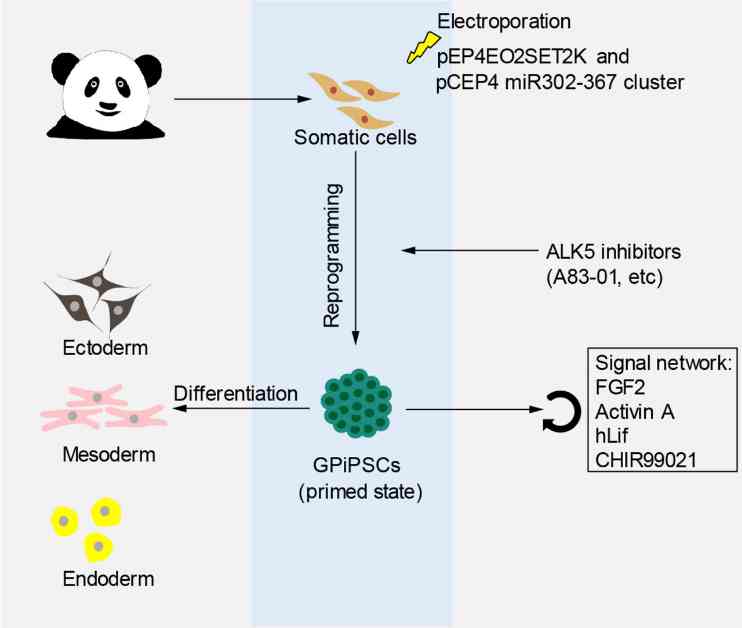
The study, recently published in the prestigious journal Science Advances, outlines the innovative approach taken by the research team to generate iPSCs from panda fibroblasts. By introducing a specific microRNA cluster to the skin cells, the scientists were able to initiate the transformation process that ultimately led to the creation of iPSCs. This method marks a significant advancement in the field of regenerative medicine research, as iPSCs have the potential to differentiate into various cell types, including those essential for organ development and reproductive functions.
Conservation Implications of iPSC Technology
The utilization of iPSC technology in conservation efforts has gained traction in recent years, with researchers exploring its application in preserving endangered species. By generating iPSCs for rare animals such as the Tasmanian devil and the northern white rhino, scientists have demonstrated the potential of this approach to contribute to species conservation and restoration.
One of the key insights from these endeavors is the species-specific nature of the process involved in creating iPSCs. Each animal species requires a tailored approach to transform fibroblasts into iPSCs, underscoring the need for customized protocols and techniques. In the case of giant pandas, the research team has developed a specialized methodology to generate iPSCs, highlighting the importance of species-specific considerations in conservation biology.
Progress Towards Giant Panda Conservation
The initiative to create iPSCs for giant pandas dates back to 2019, with the primary objective of establishing a sustainable method for propagating the species. By harnessing the regenerative potential of iPSCs as precursors to male and female reproductive cells, researchers aim to safeguard the genetic diversity and reproductive capacity of giant pandas, critical for their long-term survival.
To initiate the transformation of fibroblast skin cells into iPSCs, the research team employed a targeted approach involving the introduction of a specific microRNA cluster under optimized growth conditions. By fine-tuning the process with the appropriate transcription factors for pandas, the scientists successfully induced the conversion of fibroblasts into iPSCs, laying the foundation for further studies on their differentiation potential.
In their ongoing research, the team is rigorously testing the iPSCs to ensure their viability and functionality, particularly in terms of their ability to proliferate and differentiate into germ layers. By validating the efficacy of the iPSCs and their capacity to give rise to desired cell types, the researchers are advancing towards the ultimate goal of utilizing these stem cells for conservation purposes.
The successful generation and characterization of giant panda iPSCs represent a significant milestone in the field of conservation biology, offering a novel approach to safeguarding endangered species through regenerative medicine and stem cell technology. By transforming skin cells into versatile iPSCs with the potential to differentiate into reproductive cells, researchers are paving the way for innovative strategies to support the survival and proliferation of giant pandas and other threatened species.
As the scientific community continues to explore the applications of iPSC technology in conservation biology, the future holds immense promise for leveraging stem cell research to address the pressing challenges of species preservation and biodiversity conservation. Through collaborative efforts and innovative approaches, researchers are working towards a sustainable future for endangered species, with giant pandas serving as a flagship species in the quest for wildlife conservation and ecological sustainability.